JSON Placeholder Todos API Integration in a Simple Blog App
In this tutorial, we focus on demonstrating API integration using the ComUnity Developer Toolkit, powered by Azure API Management (APIM). Rather than starting from scratch, we will accelerate development by leveraging a template, allowing us to focus on key integrations and customisations.
A core aspect of this tutorial is utilising the APIs feature to integrate external data sources. We will connect to the JSONPlaceholder API through Azure APIM, showcasing how the Toolkit enables structured API management and integration while maintaining a well-defined data model. This hands-on guide highlights how Virtual Entities facilitate controlled interaction with third-party services, ensuring secure and efficient API exposure within the Toolkit.
What You’ll Learn
In this tutorial you will:
Set up a blog application using a predefined template to accelerate development.
Register and configure an API in the ComUnity Developer Toolkit to connect to an external data source.
Define a Virtual Entity to represent the external API within the data model.
Expose the API via the Virtual Entity by registering it in WebApiConfig.
Create a custom API class (TodosAPI) and update the controller class to handle API interactions.
Query and display JSONPlaceholder Todos within the blog application.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional blog application enhanced with external data integration, as well as the skills to extend and improve applications within the Toolkit.
Prerequisites
Access Requirements
A ComUnity user account with the necessary permissions (contact ComUnity Support if required).
A single-tenant environment is required for API integration (organisations must host their own instance of the Toolkit in Azure).
If a single-tenant instance is unavailable, users can request access to the shared ComUnity Platform environment (API management is not supported in this environment).
Technical Knowledge
C# programming skills
Familiarity with WCF Data Services, Entity Framework, and OData
Development Tools
Visual Studio 2022 (Community, Professional, or Enterprise)
Blog Application Features:
This tutorial builds a simple blog app with the following features:
Users can create, edit, and publish articles.
All users can view articles and add comments.
Authors can tag blog articles and readers can view, and comment on tagged articles.
Users can fetch and view todos from JSON Placeholder API
Walkthrough
Build and Launch a Blog from a Template
This section walks you through quickly setting up a blog application in just three steps. This forms the foundation for integrating the JSONPlaceholder Todos API in later sections.
To quickly build your blog, follow these steps:
Login into the ComUnity Developer Toolkit.
Create a project using the Blog Project template with a unique title, an illustration is shown in the following diagram:
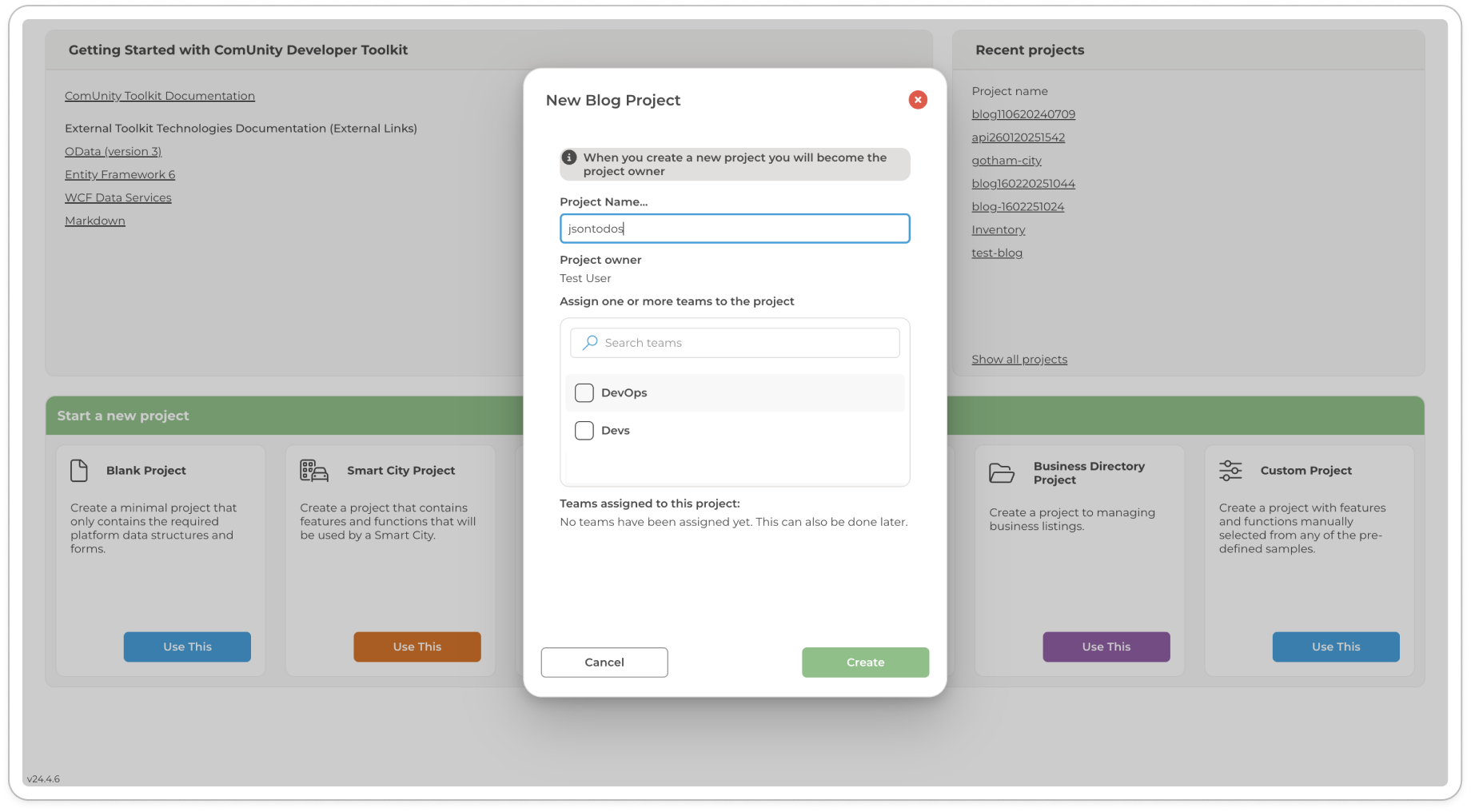
Creating a Blog app from a template Build and Launch your project the after building you will be redirected to your new app, refer to Build and Launch your project for further details. Register and log in to access the blog application.
Integrate JSON Placeholder API Todos using APIs
In this section, we will register, configure, and expose the JSONPlaceholder API within the ComUnity Developer Toolkit using the APIs feature. This process involves:
Registering the API in the Toolkit and deploying it to Azure API Management (APIM).
Defining an API operation to retrieve Todos from the JSONPlaceholder API.
Testing the API in Azure to verify the response.
Configuring a Virtual Entity to expose the Todos API within the Toolkit.
Updating Custom Classes and the WebApiConfig class to enable API access.
Building the UI to display the fetched Todos in the blog application.
By following these steps, you will integrate an external API, expose it within the data model, and render its data on a UI page. This approach demonstrates how to extend applications using the ComUnity Developer Toolkit’s API integration capabilities powered by Azure API Management.
Register the API in the Toolkit and deploy it to Azure API Management (APIM)
In the ComUnity Developer Toolkit, open your project and navigate to Third Party Services > APIs.
Enter a unique name for your API in the API display name field.
Select the option HTTP as the definition type.
Provide a relevant description.
In the Provide Web URL field, enter:
Click Add Azure API button to your project button to deploy the API to Azure API Management (APIM).
Note: The Toolkit will handle API registration and deployment based on your specifications.

Create a new Azure API Access and Review the API in Azure API Management (APIM)
Once the API is deployed, click the ellipsis (⋮) button next to View Details and select View in Azure Portal.

View an API in Azure Portal In the Azure portal, navigate to APIs under All APIs.
Use the search function to quickly locate your newly created API.
Click on the API and open the Settings tab to review its details.
Define an API Operation
Navigate to the Design tab and select Add an operation.
Provide a resource name:
Leave the HTTP Verb to GET which is the default option
In the URL field, enter the relative path:
Click the Save button to register the operation.

Defining an operation on Azure (APIM)
Test the API Operation in Azure
Go to the Test tab in the Azure API Management Portal.
Select the operation created in the previous step (/todos).
Click Send to execute the request.

Scroll down to verify the response data containing the Todos list fetched from the JSON Placeholder API
Configure Properties and Security of the Todo Virtual Entity in the Data model
Go back to the ComUnity Developer Toolkit under Data.
Create a Virtual Entity named
Todo. For detailed instructions on creating virtual entities in the Toolkit, refer to the Virtual Entities section.Leave the default options selected for Add Entity class, Add Controller class and Add controller template code.
Click the Add button to create the Todo Virtual Entity
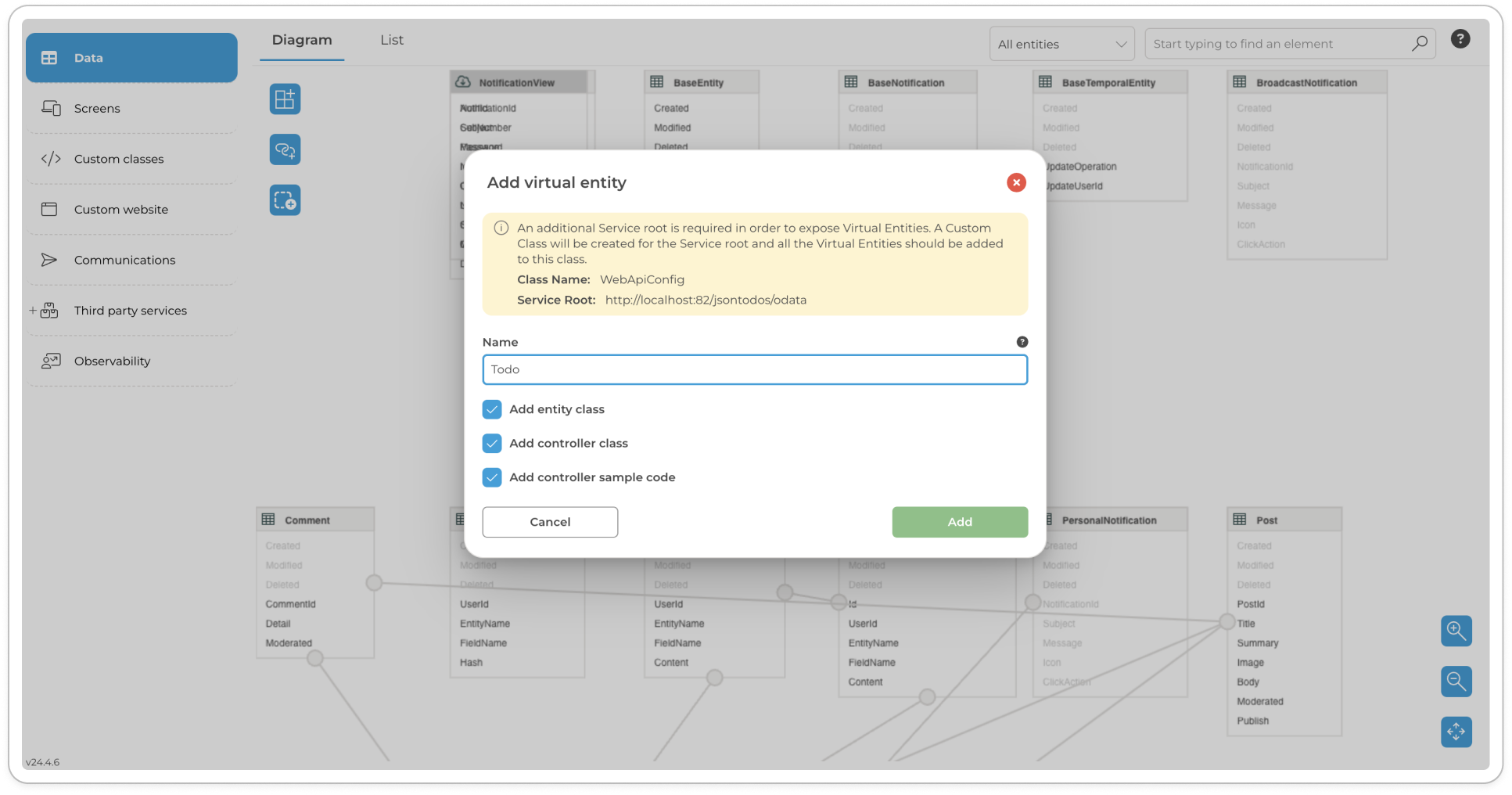
Add a virtual entity - Todo
Add the following entity fields and properties with their respective data types ensure that you delete the default primary key
TodoIdand replace it withid, refer to the section Adding Entity Fields and Configuring Field Settings for further details on how to configure fields on an entity:userId → int
id → int
title → string
completed → bool

Todo entity with its properties configured 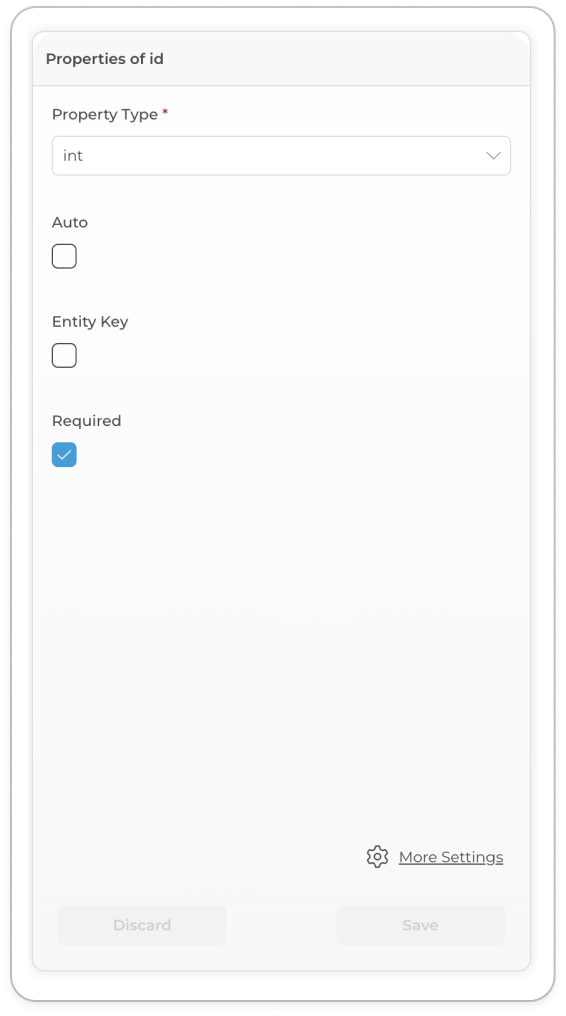
Set the permissions of the Todo Virtual Entity refer the section Setting Up Role-Based Permissions for Entities: Access Control Configuration for more information about configuring Table Security:
Select the Todo entity to activate it.
Locate Table Security setting in the Properties Editor.
Set View permission only for the User role.

Configuring role based access for the User role
Expose the Todos JSON Placeholder API via an Virtual Entities and Custom Classes
Go to Custom Classes in the Toolkit select the WebConfigApi class and register your Virtual Entity as shown below (line 23):
Create a TodosAPI class add the code below:
To replace the comment on Line 13 with your API’s URL, navigate to Third Party Services > APIs in the Toolkit, locate your API, and copy its URL.
Update the Todo entity class as shown below:
Update your controller class as shown below:
Build the UI - for more information on how to build lists in Navigation pages refer to the section Dynamic List Rendering in Navigation pages
Navigate Screens in the Toolkit and create a Todos Navigational page.
Set an icon of your choice
Add a List item to your screen
Click the List item to activate it
In the Properties Editor set the fields below with the values shown to set up your screen:
Data Path:
Item Title :
Build and Launch your project and view your todos in your application.

JSON Placeholder API Todos displayed in a Blog app
Conclusion
This tutorial has demonstrated how to integrate external APIs into an application using the ComUnity Developer Toolkit. By connecting to the JSONPlaceholder API, we successfully retrieved and displayed Todos using a Virtual Entity and the APIs feature.
Beyond this example, you can further enhance your integration skills by:
Exploring Other API Types – Try integrating APIs using OpenAPI and GraphQL API specifications to understand different API structures and query mechanisms.
Expanding Functionality – Modify the application to:
Post new Todos by extending the API integration with POST requests.
View a single Todo by configuring a GET operation with parameters.
Update or delete Todos by implementing PUT and DELETE operations.
• Customising the UI – Improve the presentation of Todos
By applying these additional enhancements, you can deepen your understanding of API integrations and extend the functionality of your application to meet real-world requirements.
Further Reading
Last updated